CHAPTER 2 (MGT300)
IDENTIFYING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Definition : A product or service that an organization's customers place a greater value on than similar offerings from a competitor.
PORTER'S FIVE FORCES MODEL
Definition : Usefool tool to aid organization in challenging decision whether to join a new industry or industry segment.
1. Buyer Power
- High- when buyers have many choices of whom to buy.
- Low- when their choices are few.
- Ways to reduce buyer power - loyalty programs
2. Supplier Power
- High- when buyers have few choices of whom to buy from.
- Low- when their choices are many
- The suppliers ability to influence the prices they charge for suppliers (including materials, labor and services).
3. Threat of Substitue products & services
- High- when there are many alternatives to a product or service.
- Low- when there are few alternatives from which to choose.
- Ideally, an organization would like to be on a market in which there are few substitues of their product or services.
4. Threat of new entrants
- High- when it is easy for new competitiors to enter a market.
- Low- when there are significant entry barriers to entering a market.
- Entry barriers : A product or service feature that customers have come to expect from organizations and must be offered by entering organization to compete and survive.
5. Rivalry among existence competitors
- High- when competition is fierce in a market.
- Low- when competition is more complacent.
- Reduce cost by using effective supply chain.
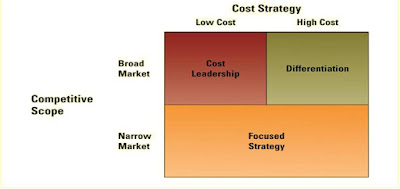
PORTER'S 3 GENERIC STRATEGIES
1. Cost Leadership
- Becoming a low-cost producer in the industry allows the companyto lower prices to customers.
- Competitors with higher costs cannot afford to compete with the low-cost leader on price.
- Superior profit
2. Differentation
- Create competitive advantage by distinguish their products on one or more features important to their customers.
- Uniques features or benefits may justify price differences or stimulate demand.
- Ex : i-care by Proton
3. Focused Strategy
The Value Chains- Targeting Business Process
- Supply Chain- a chain or series of processes that adds value to product & service for customers.
- Add value to its products and services that support a profit margin for the firm.




Comments
Post a Comment