CHAPTER 11 (MGT300)
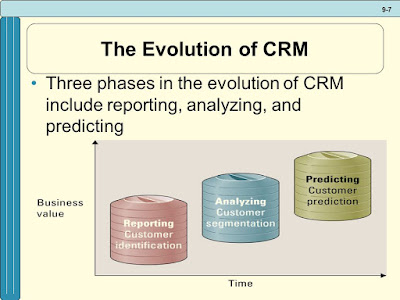
Building a Customer-Centric Organization- Customer Relationship Management Customer Relationship Management (CRM) · CRM enables an organization to: - Provide better customer service - Make call centers more efficient - Cross sell products effectively - Help sales staff close deals faster - Simplify marketing and sales processes - Discover new customers - Increase customer revenues Recency, Frequency and Monetary value · Organizations can find their most valuable customers through “RFM” – Recency, Frequency and Monetary value The Evolution of CRM · ...


